Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key symptoms associated with type 2 diabetes, shedding light on the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Before delving into the symptoms, it’s essential to understand the basics of type 2 diabetes. This metabolic disorder occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar, and its dysfunction in type 2 diabetes leads to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream.
Maybe you are interested: Products to support Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
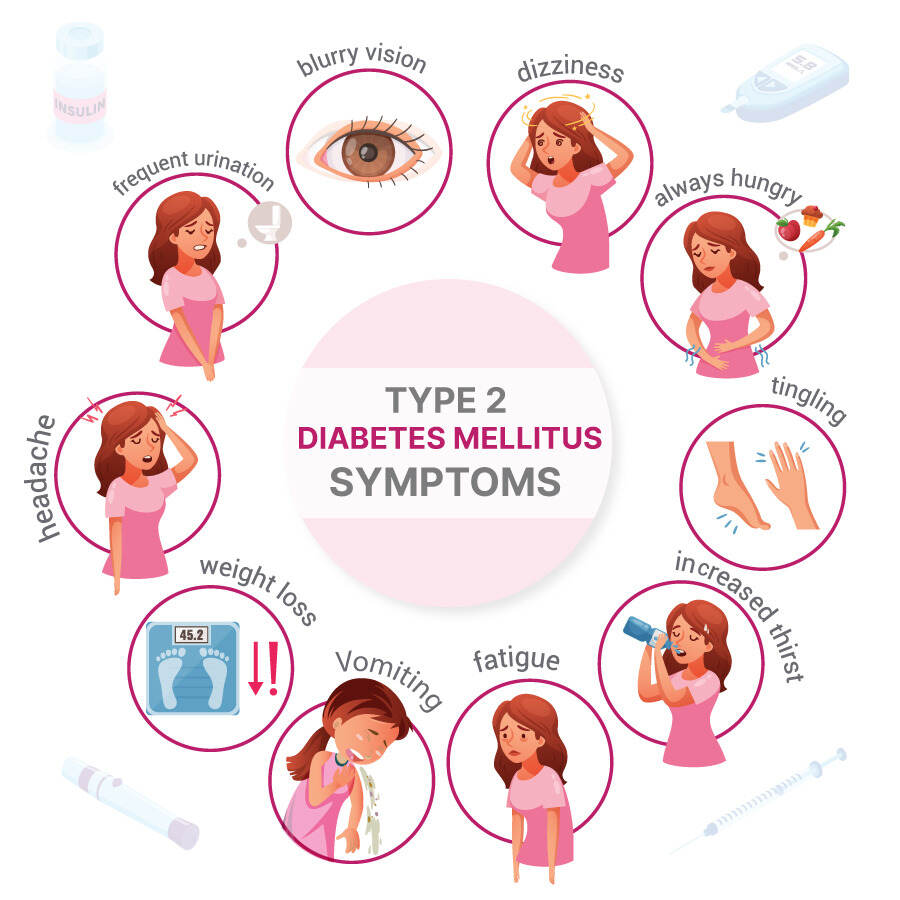
2.1 Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination:
One of the hallmark symptoms of type 2 diabetes is excessive thirst (polydipsia) and an increase in the frequency of urination (polyuria). Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to the kidneys working overtime to filter and absorb excess glucose, resulting in increased urine production. This, in turn, causes dehydration, triggering an increased need for fluids.
2.2 Unexplained Weight Loss:
Despite increased hunger and sometimes overeating, individuals with type 2 diabetes may experience unexplained weight loss. The body may break down muscle and fat for energy due to the inability to effectively use glucose. This weight loss can occur even when calorie intake remains high.
2.3 Increased Hunger:
People with type 2 diabetes often experience heightened hunger (polyphagia). The body’s inability to use glucose for energy can lead to persistent feelings of hunger, even after eating. This is a result of the body’s attempt to compensate for the lack of usable energy from glucose.
2.4 Fatigue and Weakness:
Chronic fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of type 2 diabetes. The body’s inability to efficiently convert glucose into energy can lead to a persistent feeling of tiredness. This fatigue can affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
2.5 Blurred Vision:
Elevated blood sugar levels can cause changes in the lenses of the eyes, leading to blurred vision. This symptom may come and go, particularly as blood sugar levels fluctuate. Uncontrolled diabetes can contribute to more severe and permanent eye issues over time.
2.6 Slow Wound Healing:
Impaired blood circulation and compromised immune function associated with type 2 diabetes can result in slow wound healing. Cuts and sores may take longer to heal, increasing the risk of infections.
2.7 Numbness or Tingling:
Peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of uncontrolled diabetes, can cause numbness or tingling, usually in the hands and feet. This is due to damage to the nerves that transmit sensory information.
Maybe you are interested: Top 10 Diabetes Supplements
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding the risk factors for type 2 diabetes can help individuals assess their susceptibility and take preventive measures. Some key risk factors include:
- Family History: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after the age of 45.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor.
- Inactivity: Physical inactivity is linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Race and Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans, have a higher risk.
- Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at an increased risk.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience any of the mentioned symptoms or have multiple risk factors for type 2 diabetes, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage the condition effectively and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life. Regular health check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of risk factors play pivotal roles in preventing, diagnosing, and managing type 2 diabetes. If you suspect you may have diabetes or are at risk, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance tailored to your individual needs.
In conclusion, proactive healthcare, lifestyle modifications, and awareness are key elements in the battle against type 2 diabetes. By understanding the symptoms and risk factors, individuals can take control of their health and work towards a future of improved well-being and vitality.
See more: Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Comprehensive Guide
