Welcome to : Probiotics and Diabetes: Improving Gut Health for Better Blood Sugar Control
General Introduction
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects millions worldwide and requires careful management to prevent complications. While traditional approaches like medication and lifestyle changes are pivotal, emerging research highlights the role of gut health in managing diabetes. Probiotics, beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome, have gained attention for their potential to improve blood sugar control. This article delves into how probiotics can enhance gut health and contribute to better diabetes management.
Understanding Gut Health and Its Importance
The Gut Microbiome
The human gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. These microorganisms play a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing various diseases, including diabetes.
Gut Health and Diabetes
Research indicates a strong link between gut health and diabetes. An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to insulin resistance and inflammation, both of which are key factors in the development and progression of diabetes. Therefore, improving gut health through probiotics can potentially enhance blood sugar control and overall diabetes management.
Probiotics: A Key to Improving Gut Health
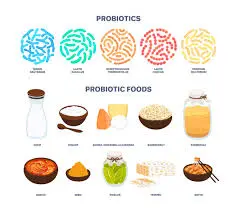
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Common sources of probiotics include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and dietary supplements. These beneficial bacteria help maintain a healthy balance in the gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall health.
How Probiotics Work
Probiotics work by colonizing the gut and outcompeting harmful bacteria. They produce substances that inhibit the growth of pathogens, enhance the gut barrier function, and modulate the immune system. These actions contribute to a balanced gut microbiome, which is essential for improving gut health and potentially managing diabetes.
Probiotics and Blood Sugar Control
Mechanisms of Action
- Improving Insulin Sensitivity:
– Probiotics can enhance insulin sensitivity by reducing inflammation and improving the function of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Certain probiotic strains have been shown to increase the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which play a role in regulating blood sugar levels.
- Reducing Inflammation:
– Chronic inflammation is a common issue in individuals with diabetes. Probiotics can help reduce inflammation by modulating the immune response and promoting the production of anti-inflammatory compounds. This reduction in inflammation can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Enhancing Gut Barrier Function:
– A healthy gut barrier prevents the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream, which can trigger inflammation and insulin resistance. Probiotics strengthen the gut barrier, reducing the risk of these complications and supporting better blood sugar control.
>>>> Refer Blood Pressure Support Product
Evidence from Research
Several studies have explored the impact of probiotics on blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. For example, a study published in the Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders found that probiotic supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels and improved insulin sensitivity in participants with type 2 diabetes. Another study in the “British Journal of Nutrition” reported that probiotics improved glycemic control and reduced markers of inflammation in individuals with gestational diabetes.
>>>> Visit Diabetes Freedom Product- Top Diabetes Supplement Product
Choosing the Right Probiotics for Diabetes
Selecting Effective Strains
Not all probiotics are created equal, and different strains offer varying health benefits. For diabetes management, strains such as **Lactobacillus acidophilus**, **Bifidobacterium lactis**, and **Lactobacillus casei** have shown promising results in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. It is essential to choose probiotic supplements that contain these specific strains to achieve the desired benefits.
Dosage and Administration
The effectiveness of probiotics depends on the dosage and duration of supplementation. Research suggests that a daily intake of at least 10 billion colony-forming units (CFUs) is necessary to achieve significant health benefits. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on individual needs and health conditions.
Probiotic-Rich Foods
In addition to supplements, incorporating probiotic-rich foods into the diet can enhance gut health and support diabetes management. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso are excellent sources of probiotics. Regular consumption of these foods can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and improve overall health.

Practical Tips for Incorporating Probiotics
Gradual Introduction
Introduce probiotics gradually into your diet to allow your gut to adjust. Start with small amounts and gradually increase the intake over time.
Consistency is Key
Consistency is crucial when it comes to probiotics. Make sure to include probiotic-rich foods or supplements in your daily routine to maintain a balanced gut microbiome.
Combine with Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for probiotics. Consuming prebiotic-rich foods like bananas, garlic, onions, and whole grains can enhance the effectiveness of probiotics and support a healthy gut.
Conclusion
Improving gut health through probiotics offers a promising avenue for better diabetes management. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and strengthening the gut barrier, probiotics can contribute significantly to blood sugar control. For individuals with diabetes, incorporating probiotics into their diet, either through supplements or probiotic-rich foods, can lead to improved overall health and well-being. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and conditions. Embrace the power of probiotics and take a proactive step towards managing diabetes more effectively through improved gut health.
Read more: Top 10 Diabetes Supplements – How To Reduce Blood Sugar Level Immediately

