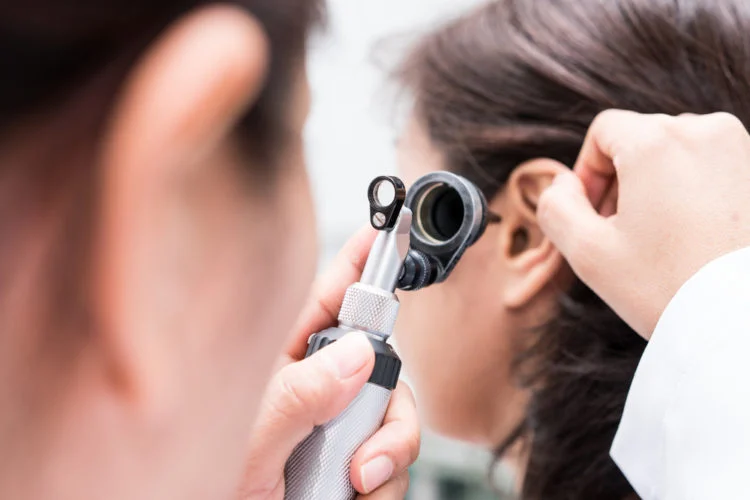
When the inner ear becomes infected and inflamed, it can lead to disturbances in balance, also known as Ménière’s disease. So, what exactly is this inflammatory condition? Is it dangerous? Please refer to the following article.
What is Ménière’s Disease? Ménière’s disease is a disorder of the inner ear. The two vestibular nerves in the inner ear are responsible for sending information to the brain to help navigate space and control the body’s balance. When one of these nerves becomes inflamed, it leads to Ménière’s disease.

This inflammatory condition has two forms:
Viral Ménière’s Disease
This type of infection is more common than bacterial causes, but doctors have limited information about this disease. Some viruses seem to be associated with Ménière’s disease, including those causing measles, mumps, hepatitis, as well as viruses responsible for chickenpox, shingles, or herpes zoster.
If you have viral Ménière’s disease, you’ll typically experience symptoms in one ear only and often recover quickly. However, the disease can recur without warning.

Click here to see Product Support Your Ears
Bacterial Ménière’s Disease Bacteria cause Ménière’s disease in two ways:
Bacteria causing middle ear infections produce toxins that invade the inner ear and cause inflammation and swelling. Infections in the bone surrounding the inner ear produce toxins that cause similar symptoms. Additionally, chronic middle ear infections can also lead to this condition.
What Are the Symptoms of Ménière’s Disease? This condition not only affects hearing but also induces dizziness. Sometimes, you may experience more severe signs of the disease, such as vertigo, making you feel like everything around you is spinning.
Other symptoms of Ménière’s disease include:
Blurred vision Feeling off balance, as if about to fall Feeling light-headed or floating Nausea and vomiting Ringing in the ears or hearing loss These symptoms often occur unexpectedly. For instance, you may notice unusual signs upon waking up, causing distress and anxiety. If you experience difficulty maintaining balance or vision problems, seek medical attention promptly.
Causes of Ménière’s Disease Ménière’s disease can occur at any age. However, certain factors may contribute to its development, such as:
Respiratory illnesses like bronchitis Viral infections in the inner ear Gastric viruses Herpes viruses Bacterial infections, including bacterial middle ear infections Infectious organisms such as Lyme disease-causing bacteria You’re at a higher risk of developing Ménière’s disease if you:
Smoke Consume excessive alcohol Have a history of allergies Experience frequent fatigue Are under extreme stress Take certain prescribed medications Use over-the-counter drugs (especially aspirin) How Is Ménière’s Disease Diagnosed? In reality, there are numerous causes of dizziness, making it challenging to diagnose Ménière’s disease based solely on this symptom.
To diagnose the condition, doctors rely on symptoms, medical history, and the patient’s physical examination results.
Click here to see Product Support Your Ears
Some tests that aid in diagnosing Ménière’s disease include:
Physical examination – The doctor may request head or body movements and examine the ears for signs of inflammation and infection. Hearing tests – You’re at a higher risk of developing the disease if you experience hearing loss. Additionally, the doctor will examine your eyes. Uncontrollable eye movements often indicate abnormal vestibular system function.
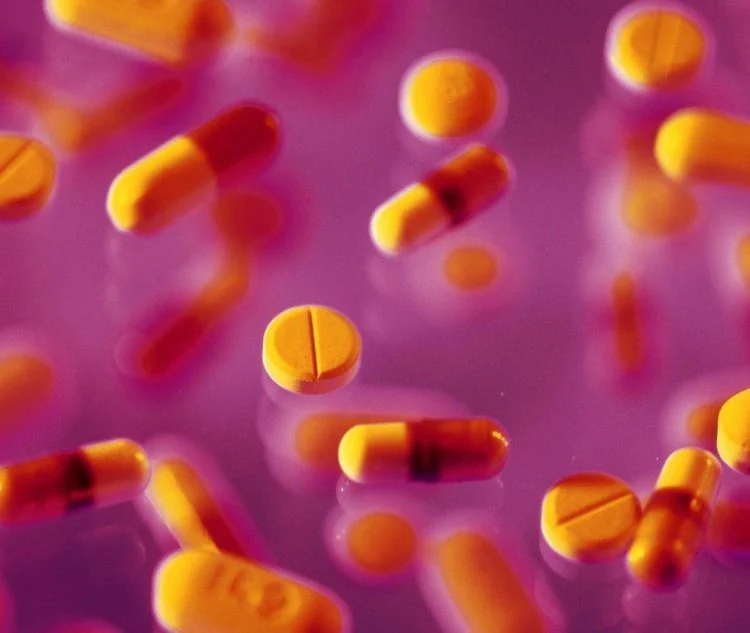
Treatment Options for Ménière’s Disease Several medications can help alleviate disease symptoms, such as:
Prescription antihistamines like desloratadine Medications to reduce dizziness and nausea, such as meclizine Sedatives like diazepam Corticosteroids such as prednisone Over-the-counter antihistamines like fexofenadine, diphenhydramine, or loratadine If you have an infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Ensure you take antibiotics as directed to avoid any unwanted side effects.
Apart from medication, you can implement some measures to reduc
Avoid sudden position changes or abrupt movements. Stay still when experiencing dizziness. Rise slowly from lying down or sitting positions. Avoid looking at bright screens, TVs, or flickering computer monitors during dizzy spells. If you experience dizziness while lying down, try sitting up and keeping your head still. Dim lighting is preferable for your symptoms rather than complete darkness or bright lights.
Persistent dizziness may necessitate physical and occupational therapy to help improve balance.
Recovery In most cases, symptoms subside within 1-3 weeks, and you’ll fully recover within a few months. During this time, symptoms like dizziness and vomiting may hinder your ability to work, drive, or participate in social activities.
Click here to see Product Support Your Ears
If your symptoms persist after several months, your doctor may request additional tests to rule out other underlying conditions.
Most people experience only one episode of Ménière’s disease, and it rarely becomes a chronic condition.